Rapid Impact Compaction is a ground improvement technique that densifies the soil by pounding it at high frequency with a medium sized pounder.

Presentation and key elements
What is Rapid Impact Compaction and why do we use it?
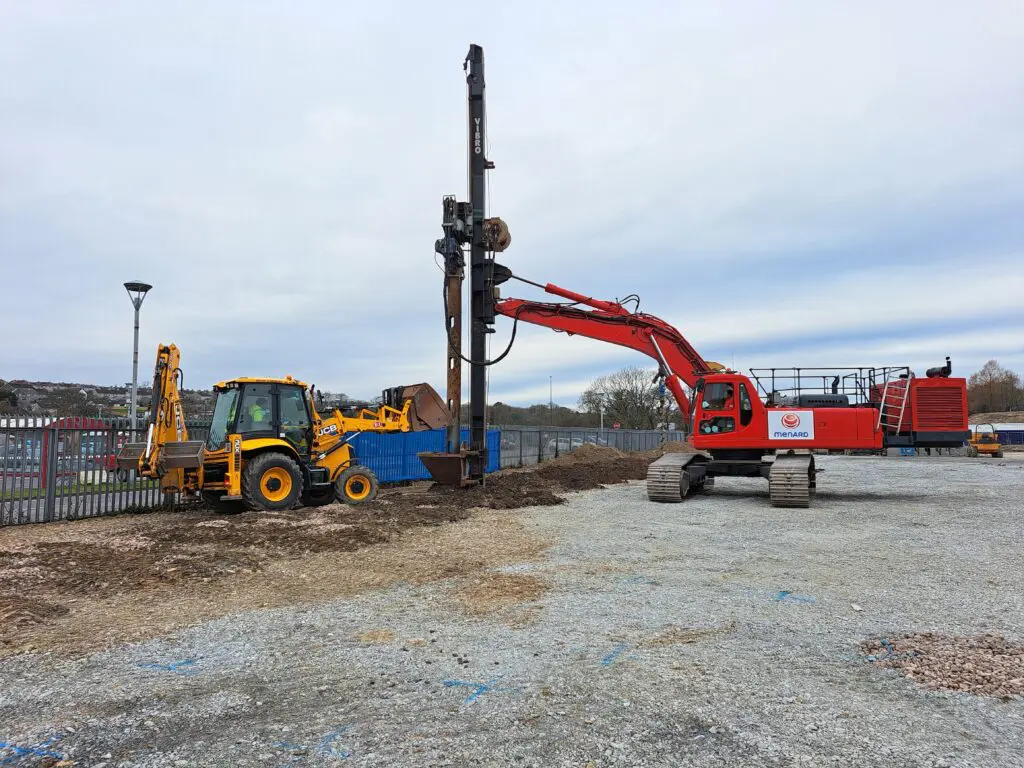
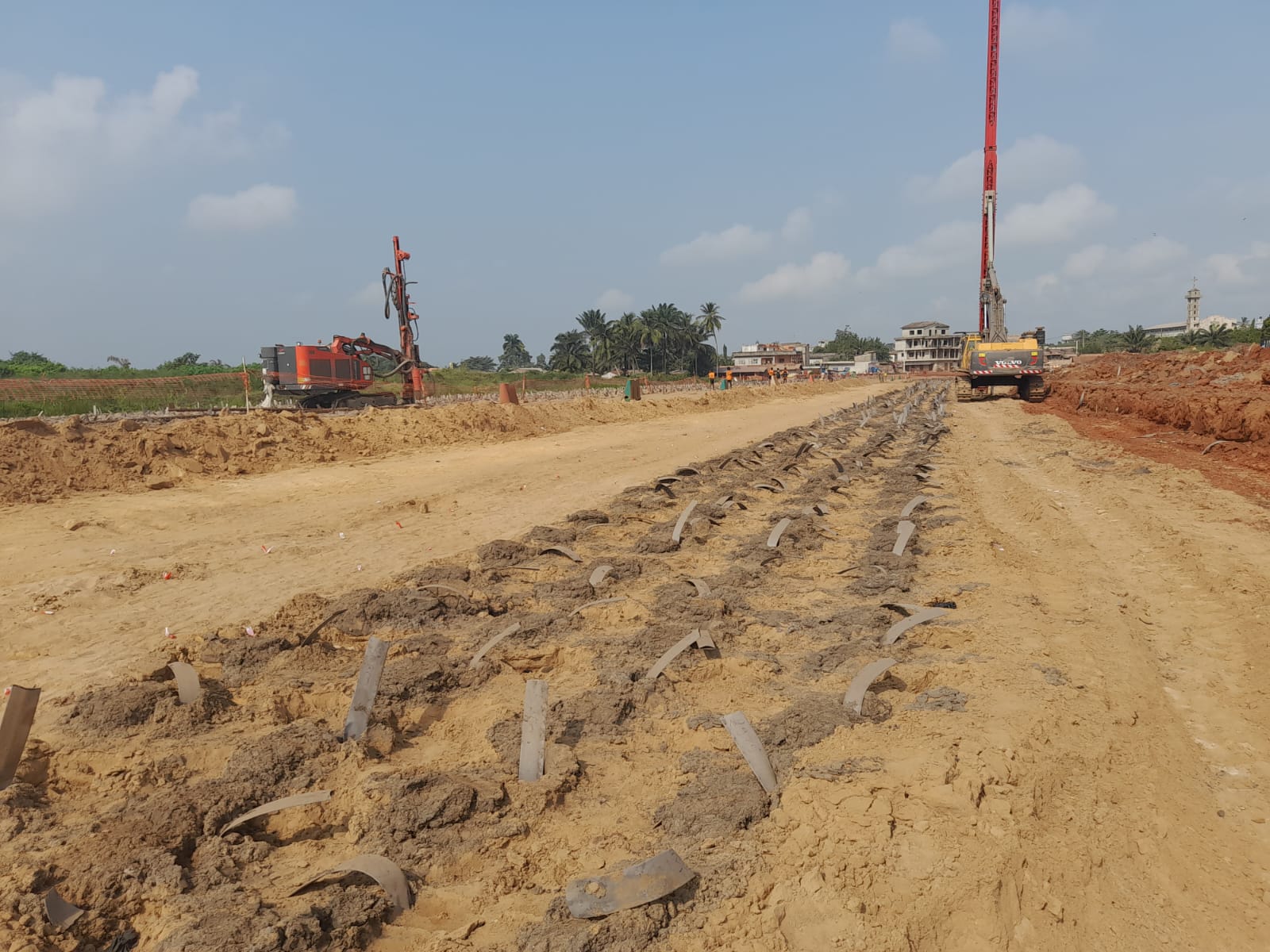
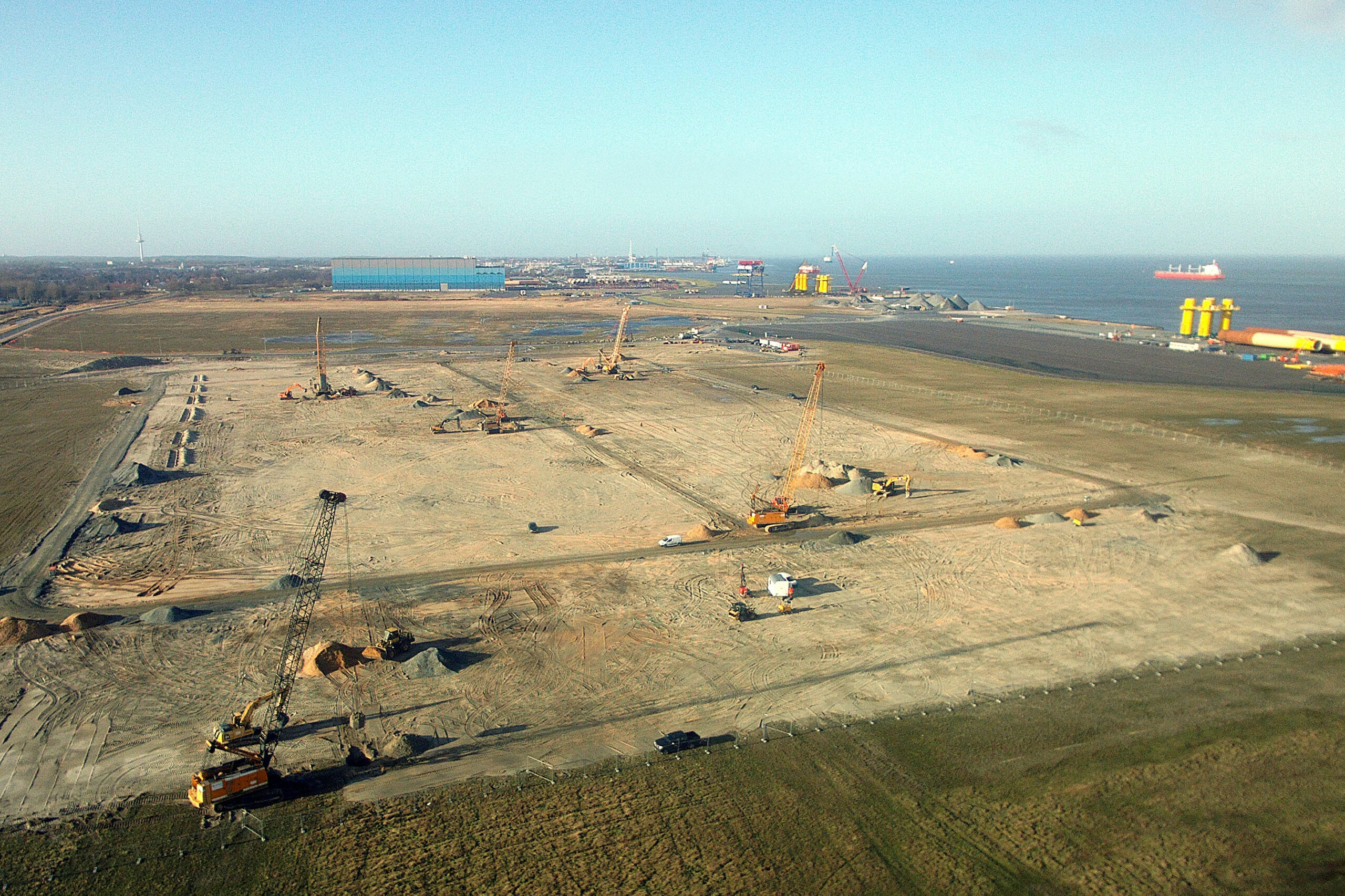
RIC is a high-frequency, controlled energy, soil compaction technique used to densify surface layers of soils (to a depth of 5 to 7 meters in most cases) with minimum impact on the immediate worksite environment. Rapid Impact Compaction is widely used to densify loose granular soils (sand or gravel) as well as loam fill and industrial brownfield sites for surface compaction, foundations and floor slab support, liquefaction mitigation and waste stabilisation.
Basic principle of Rapid Impact Compaction
The principle of the technique which is similar to other compaction / densification techniques is a transmission of energy into a compressible / loose soil layer in order to improve its geotechnical properties.
Execution of Rapid Impact Compaction
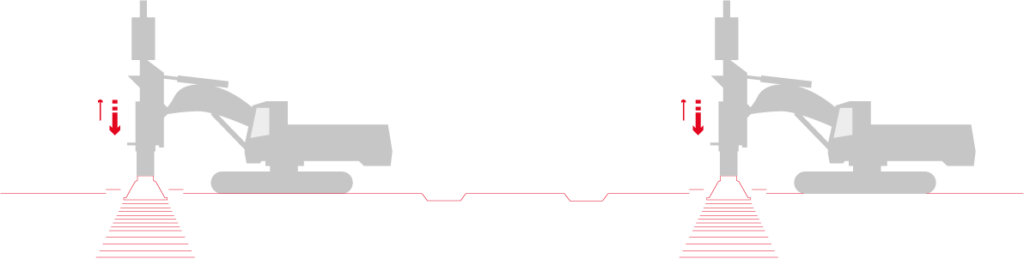
A compaction plate is placed on the ground to be treated. A hydraulic hammer, generally weighing less than 10 to 15 tonnes, is fitted to an excavator and used to transmit compaction energy to the soil via repeated impact. Without specific site precautions, a safe working distance to sensitive structures can usually be defined on the order of 8 to 10 m, as a distance of 5 to 6 m can usually be adopted for classical structures. At that distance, noise levels are lower than 90 dBA.